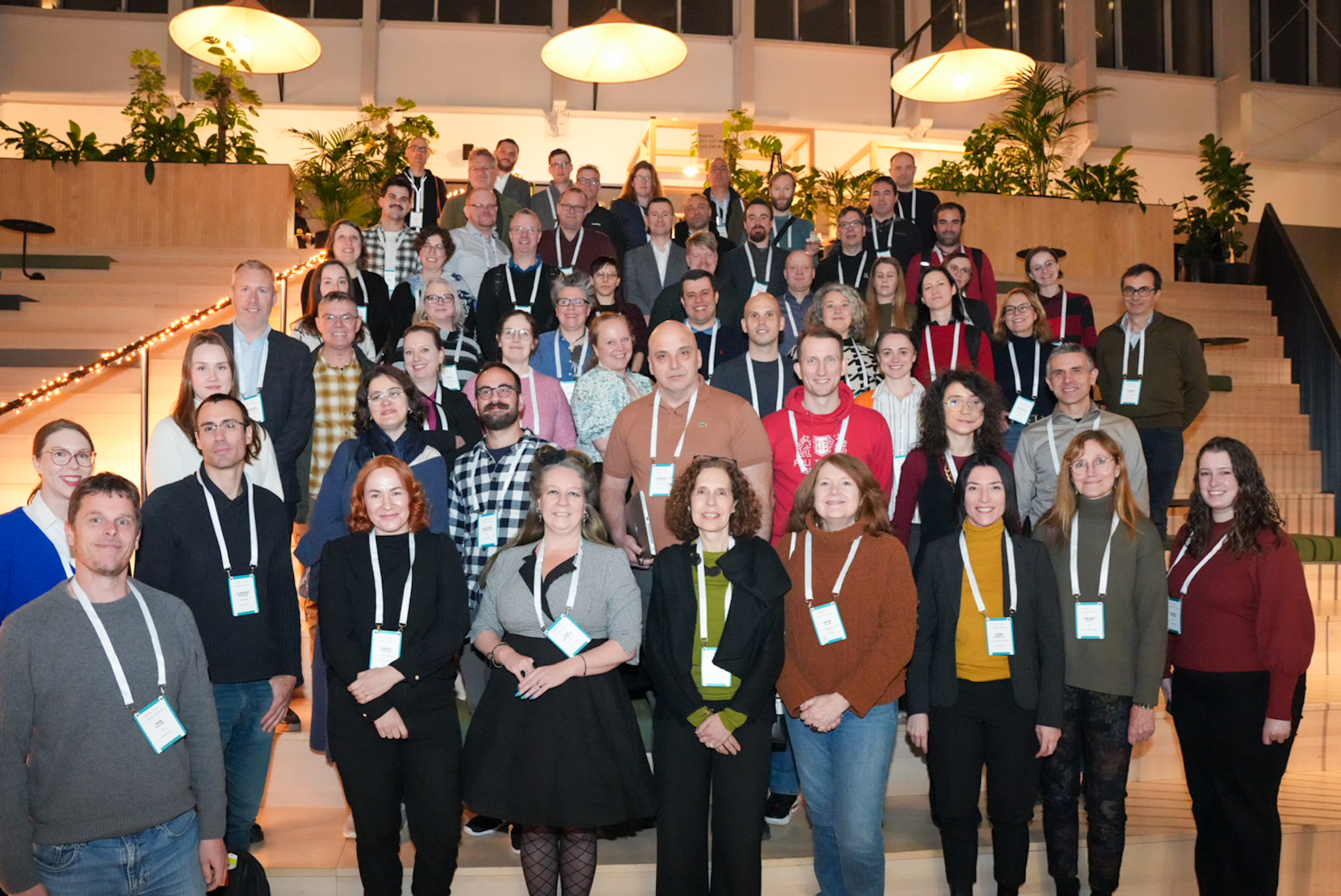
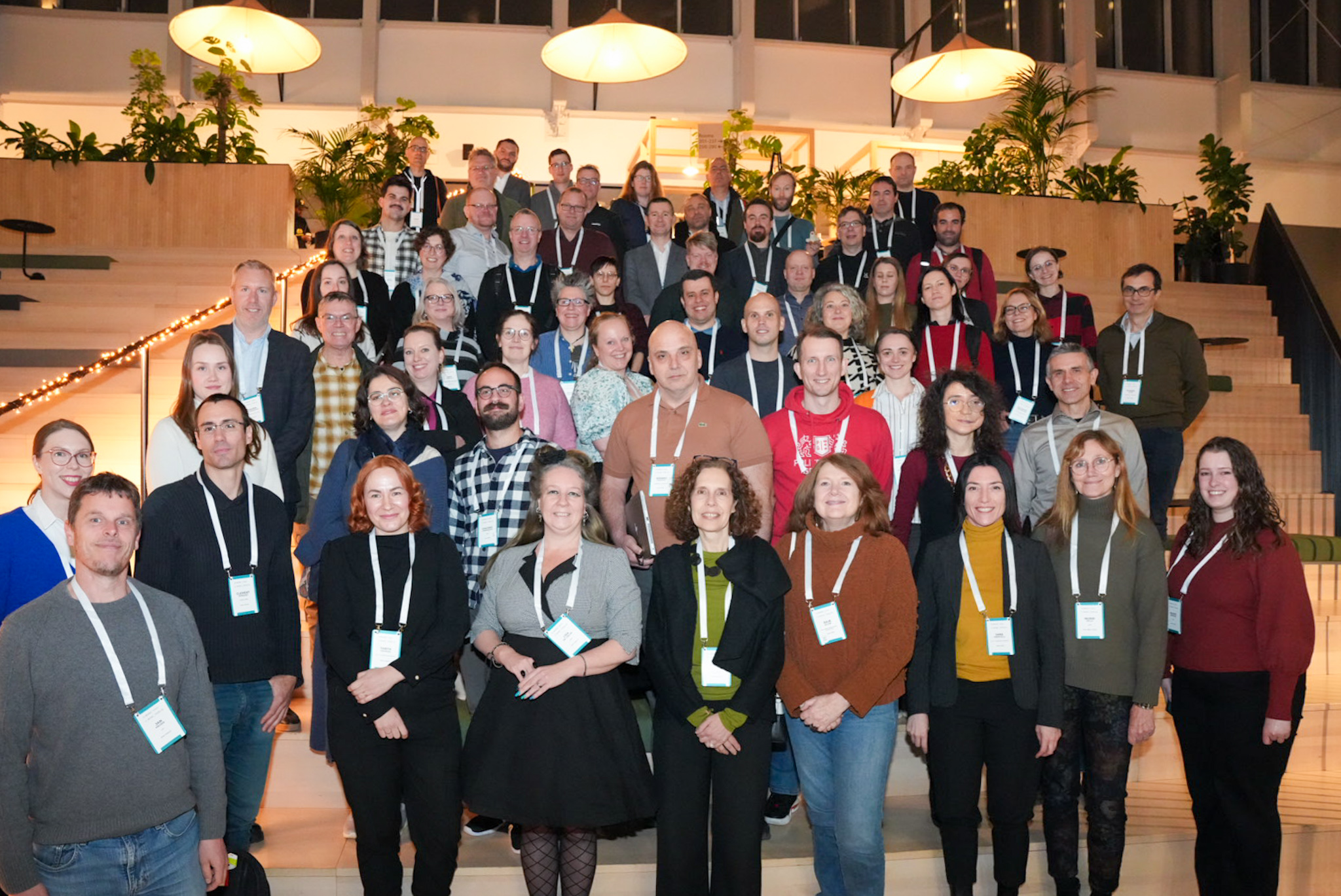
What is EOSC EDEN?
The EOSC EDEN project (grant agreement nr.101188015) seeks to enhance digital preservation strategies at European and National level. At its core, the project will create a comprehensive framework to identify what data are candidates for digital preservation. This involves setting standards and protocols for long-term data preservation, which will be determined through an assessment of data usage, quality, and the data’s benefits to science and society.
In addition to the framework, the EOSC EDEN project aims to develop a model for re-appraisal of data throughout its lifecycle. The model’s usability and practicality will be assessed through relevant communities (the early adopters), which will also help in developing tools and services to automate certain preservation actions. The model for re-appraisal will support the framework for digital preservation by ensuring that preservation efforts remain relevant over time.

How will this project contribute to the European Open Science Cloud?
All of this will be done in the context of EOSC, the European Open Science Cloud, which is developing a web of FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) data and services for science in Europe. Hence, the EOSC EDEN project will build a registry to integrate tools and services from trustworthy repositories into the EOSC, enhancing and developing new services to automate preservation and curation actions. The project will provide training and outreach activities to engage other relevant communities in testing and validating the project outcomes.
“EOSC EDEN has the opportunity to become the reference point in Europe for digital preservation and curation practices. Different communities and scientific disciplines tend to have their own data quality standards, curation procedures and digital preservation methodologies. Our mission is to understand the current landscape, identify common standards and practices, and provide solutions and new approaches that help institutions in selecting and preserving high-quality FAIR research outputs. All this will also help to reduce the costs of preservation and increase the future re-usability of data,”says Anu Märkälä, EOSC EDEN Coordinator and Project Manager, CSC.
The EOSC EDEN consortium is a diverse assembly of 16 organizations that have expertise in digital preservation, data quality, curation, and FAIR data management and services. Additionally, seven scientific disciplines are represented in the consortium: Climate Simulations; Earth and Environmental Sciences; Food Sciences; High-Energy Physics; Life Sciences and Bioinformatics; Linguistics; and Social Sciences.